Acetic Acid
Other Names:
Glacial acetic acid
Ethanoic acid
General Information:
Structure:
![]()
CAS Number: 64-19-7
Molecular Weight: 60.05 g/mol
Appearance: Colorless liquid
Chemical Formula: CH3CO2H
Melting Point: 16-17 C
Boiling Point: 118-119 C
Density: 1.049 g/mL at 25 C
Acidity (pKa): 4.76
The common name for undiluted acetic acid is glacial acetic acid. With a melting/freezing point of around 16 C, acetic acid is not a suitable solvent for reactions that require cooling. In fact, when removing acetic acid by rotovap it tends to crystallize on the cold finger of the rotovap rather than dripping into the collection flask as a liquid.
Acetic acid is sometimes used as a polar protic solvent. When it is used as a solvent, it is often used for reactions that involve carbocation intermediates.
Acetic acid is a weak monoprotic acid and has a pKa of 4.76. As a weak acid, acetic acid is sometimes used to quench basic reactions, or to adjust the pH of a mixture.
Common Uses:
Solvent in nitration reactions
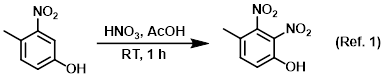
Procedure excerpt:
To a solution of the SM (10 g, 65.36 mmol) in AcOH (60 mL) was slowly added HNO3 (3.3 mL, 78.4 mmol) at 0 C. The reaction mixture was . . .
Reagent/catalyst in reductive aminations
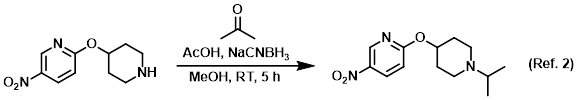
Procedure excerpt:
To a solution of 10% AcOH in MeOH was added the SM (1 equiv) and dry acetone (5 equiv). The solution was stirred at RT 1 h, after which time . . .
Solvent/co-solvent in the iron catalyzed nitro reductions
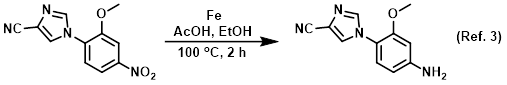
Procedure excerpt:
To a solution of the SM (689 mg, 2.82 mmol) in EtOH (15 mL) was added AcOH (7.5 mL) and Fe (630 mg, 11.29 mmol). The resulting mixture was brought to 100 C and . . .
Solvent in brominations (especially alpha-bromination)
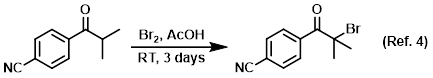
Procedure excerpt:
To a mixture of the SM (2.4 g, 13.86 mmol) in AcOH (50 mL) was added Br2 (0.80 mL, 15.53 mmol). The mixture was stirred at RT . . .
Reagent for quenching reactions
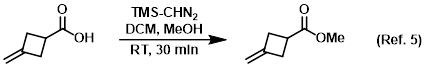
Procedure excerpt:
. . . stirred at RT for 30 min. The mixture was quenched with AcOH (0.45 mL) and concentrated in vacuo. The resulting material was purified . . .
Acid for adjusting pH
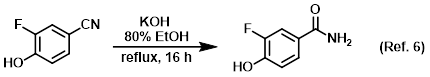
Procedure excerpt:
. . . The reaction mixture was cooled to RT and concentrated in vacuo. The mixture was diluted with H2O, acidified with AcOH, and extracted with EtOAc . . .
Additive in HPLC purifications
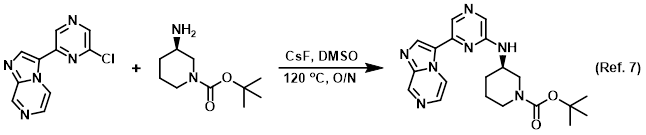
Procedure excerpt:
. . . in DMSO (0.9 mL) was heated to 120 C overnight. The crude product was filtered and purified by HPLC (H2O/ACN with AcOH) . . .
Reagent for forming acetate salts of compounds
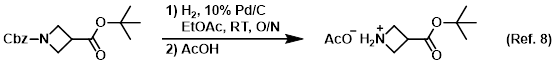
Procedure excerpt:
. . . added AcOH (28.9 g, 0.480 mol). The mixture was concentrated in vacuo (maintaining the temp below 50 C) to provide the product as the carboxylate acetic acid salt. . . .
Safety:
Concentrated acetic acid (AcOH) is corrosive to the skin. Nitrile gloves have been shown to provide much better protection against acetic acid compared to latex gloves.
References:
1) Patent Reference: WO2014149164, page 386, ![]() (23.7 MB)
(23.7 MB)
2) Patent Reference: WO2007084786, page 112, ![]() (9.4 MB)
(9.4 MB)
3) Patent Reference: WO2011014535, page 39, ![]() (17.3 MB)
(17.3 MB)
4) Patent Reference: WO2011017578, page 154, ![]() (8.3 MB)
(8.3 MB)
5) Patent Reference: WO2015129926, page 108, ![]() (21.5 MB)
(21.5 MB)
6) Patent Reference: WO2012069948, page 63, ![]() (3.9 MB)
(3.9 MB)
7) Patent Reference: WO2010016005, page 84, ![]() (3.9 MB)
(3.9 MB)
8) Patent Reference: WO2011017578, page 127, ![]() (8.3 MB)
(8.3 MB)
9) Wikipedia: Acetic acid (link)
10) www.sigmaaldrich.com: Glacial acetic acid (link)
11) www.emdmillipore.com: Acetic acid (glacial) 100% (link)