Boc Protection
(Boc2O + Base)
Mechanism:
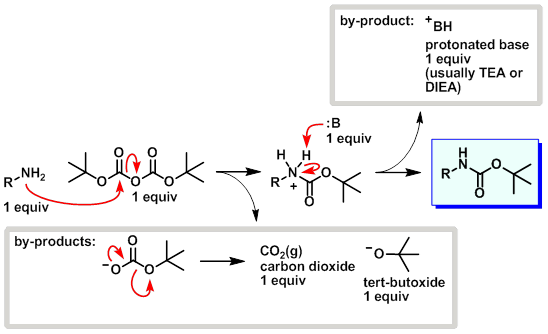
Steps:
- The amine attacks a carbonyl site on di-tert-butyl dicarbonate (Boc2O) resulting in tert-butyl carbonate leaving as a leaving group.
- The base (usually TEA or DIEA) picks up the proton from the protonated amine.
- tert-Butyl carbonate breaks down into CO2 (gas) and tert-butoxide.
Key Points:
- The CO2 gas that forms during the reaction should be allowed to escape. Don't run boc protections in closed systems.
- Base isn't needed for a boc protection reaction to progress (see Boc Protection Boc2O).
- tert-Butoxide is actually a stronger base than TEA (or DIEA) therefore in the end the proton should end up on tert-butoxide forming tert-butanol.